![]()
Chemical Reactions I: Net ionic equations
| A combustion reaction is demonstrated by the burning of magnesium in air, emitting a brilliant light and intense heat. | .jpg) |
.jpg) |
This reaction demonstrates the difference of solubility of copper chloride in water, and then with addition of sodium hydroxide. |
| Various clear solutions are mixed to form precipitates. | .jpg) |
.jpg) |
When calcium carbonate is added to water, it is practically insoluble. When added to acid it dissolves producing carbon dioxide. |
4.5 Net Ionic Equations– No driving force for reaction = no reaction |
|
|---|---|
| Two chemicals are mixed together resulting in no reaction. | .jpg) |
 (141x250).jpg) |
The conductivity of different solutions and liquids is compared qualitatively using a light bulb conductivity meter. Alternatively, the Vernier Salinity sensor can be used. |
| The conductivity of acetic acid and ammonia are measured separately. The solutions are then mixed and the conductivity is measured again. A mixture of the solutions produces a stronger electrolyte solution. Alternatively, the Vernier Salinity sensor can be used. |  (250x141).jpg) |
 (250x141).jpg) |
The reaction of magnesium metal with different acids is used to measure their relative strengths. Hydrogen gas is formed during the reaction. Stronger acids will produce a more vigorous reaction with more bubbling. The increased bubbling with acids of different concentrations also demonstrates the affect of concentration on a reaction. |
| The relative pH of some foods and household chemicals is illustrated by the use of Universal indicator. A Vernier pH meter can be used for more quantitative measurements. |  (250x141).jpg) |
|
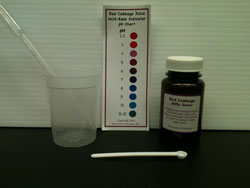
The relative pH of some foods and household chemicals is illustrated using red cabbage juice indicator. |
 (250x141).jpg) |
Demonstration of how to clean up insoluble metal hydroxides in a solution with addition of acid. The copper hydroxide solution made in demo 4.2 or the iron hydroxide solution made in demo 4.4 can be used for this reaction. Milk of Magnesia is used in the second reaction. |
| Calcium carbide is added to water in a balloon. The acetylene gas produced in the reaction is ignited producing a loud explosion. |  (250x141).jpg) |
 (250x141).jpg) |
Observation of the oxidation of zinc metal by hydrochloric acid to form hydrogen gas and zinc chloride. |